Riding atop the Long March-2F Y12 carrier rocket, the Shenzhou-12 manned spacecraft was successfully launched into preset orbit on Thursday morning from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in the Gobi Desert in Southwest China's Gansu Province, signifying that China's Tianhe space station core cabin module is now only hours away from receiving its first batch of astronauts for their three-month stay.
With the aim of ferrying a three-strong crew consisting of veteran astronaut Nie Haisheng, who visited space twice in October 2005 and June 2013, Liu Boming, who had flew to space and participated the country’s first spacewalk together with Zhai Zhigang during the Shenzhou-7 mission in 2008 and one new face Tang Hongbo to the orbiting space module of Tianhe, Shenzhou-12 or the “Divine Vessel” entered its designated orbit after separating with the rocket 573 seconds after its launch, declaring full success for the launch mission, Global Times learned from China’s Manned Space Agency.
The three astronauts of the Shenzhou-12 mission, who were selected from China's first and second batch of astronauts, will stay in space for three months, during which they will carry out tasks including repair and maintenance, appliance switch and scientific operation of payloads.
It was the first time in nearly five years that China has sent astronauts into space, and is the first crewed flight mission and third leg of the country's total 11 space launch missions of the intensive space station construction phase.
China previously sent the space station's Tianhe core cabin module via Long March-5B carrier rocket on April 29, and the Tianzhou-2 cargo spacecraft via Long March-7 on May 29.

Shenzhou-12 successfully launched for manned mission to space on June 17, 2021 Graphic: GT
Vessel of life
According to Gao Xu, the deputy director designer of the Shenzhou-12 with the project prime contractor China Academy of Space Technology (CAST), the development of the manned spacecraft followed the highest standards in the country's space industry.
The Shenzhou-12 is made up of three sections—an orbiter module, a return module and a propelling module, and has 14 sub-systems onboard. Gao referred to the spacecraft with a term of affection: "Vessel of life", as it will not only ferry three astronauts to the orbiting Tianhe core module, but is also expected to carry them home to Earth in approximately 90 days.
Making the safety of astronauts a priority, the research team of the Shenzhou-12 mission has also developed a new emergency response system to ensure that the astronauts can be rescued both in space and at the launch site.
According to CAST, two Shenzhou vessels have been transported to the launch site, which means that Shenzhou-12 has a back-up that will stand by in the event of an emergency. The latter has the capability of being launched in eight and a half days to carry out space rescue work after the launch of the former.
Compared to its crewed mission predecessor from five years ago, whose exterior was dull grey color, the Shenzhou-12 has a new shining silver look, due to the application of a new type of heat-resistant coating.
The Shenzhou-12 will spend longer in orbit than previous Shenzhou spacecraft, meaning it will face with a harsher space environment. For example, it Sun-exposed side will reach 90 degree Celsius on the surface and minus 30 degree Celsius on the far side from the Sun, according to CAST.
The new coating that uses new materials will help protect the inside of the craft from this harsh environment, and prevent it from affecting the living conditions of astronauts and working conditions for multiple precision appliances on board, said the coating designers.
The new coating will also provide protection against a range of radiation in space around the clock, they said.
As the only manned space launch vehicle, Long March-2F is 58.3 meters in height with four 2.25-diameter-boosters and a 3.35-meter-diameter core stage.
The rocket is the go-to type for China's manned space program, and with Thursday's successful launch, it has scored a perfect launch rate in all 14 deployments including seven manned flight missions, five uncrewed spacecraft flight missions and the launch of two space labs (Tiangong-1 and -2.)
The development of the rocket type was approved by state authorities in 1992, the same year the country's manned space project was approved. Long March-2F made its successful maiden flight in 1999.
According to developers of the rocket from the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology (CALT), the escape tower - the lightning rod-like device atop the rocket body - will enable astronauts to get out of the rocket from 15 minutes before launch to 120 seconds after take-off in emergency situations.
To make the flight safer, the Long March-12 developers have further enhanced the rocket's escape mechanism, adding a new ignition function to the launch safety system.
CALT designers said that once an emergency occurs, the escape system will be activated, pulling off the return module of the spacecraft from the malfunctioning rocket. The module will then open its parachute before landing on the ground.
However, the parachute system can be easily affected by the wind near the ground.
To address that issue, the new ignition system will enable the escaping craft to fly in a direction perpendicular to the wind direction, so as to make the process safer and more flexible.
This improvement has enhanced the rocket security assessment value to a world-leading 0.99996. "That's to say, there would be four failed escapes in 100,000 launches," disclosed Chang Wuquan, one of the system's designers.
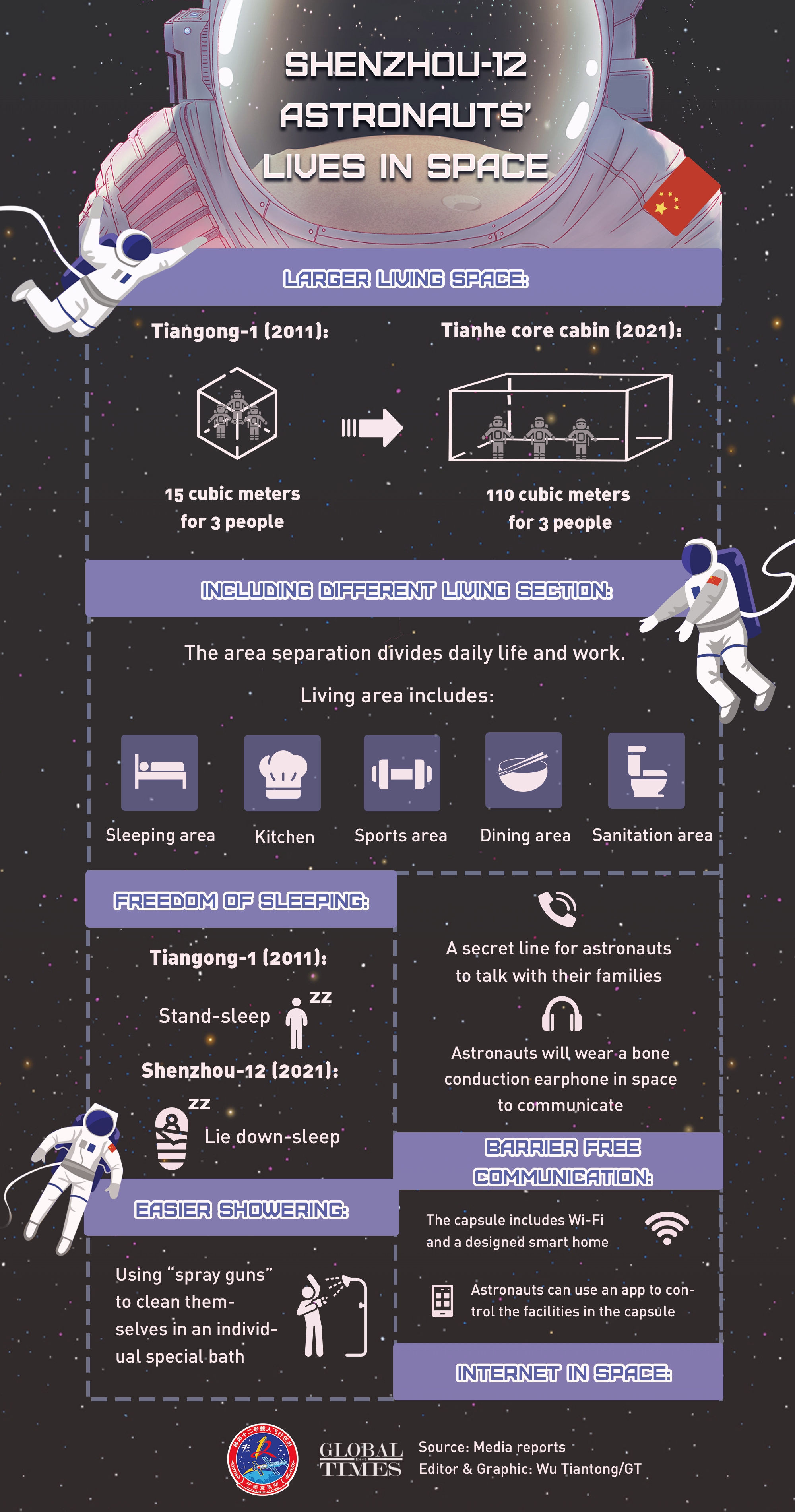
Shenzhou-12 astronauts’ lives in space Infographic: Wu Tiantong/GT
Breakthroughs to accomplish
According to CAST, Shenzhou-12 will attempt a fast and automated rendezvous and docking with the Tianhe core cabin for crewed spacecraft, a first in the country's history which can take place only 6.5 hours after the launch.
During the mission of the Tianzhou-2 cargo spacecraft, China managed to pull off a fast but smooth automatic docking of the cargo ship with the Tianhe module within only eight hours after launch.
Pang Zhihao, a Beijing-based senior space expert, hailed the breakthrough technology, saying it would tremendously benefit crewed missions, as it would save astronauts from longer stays in the narrow space onboard the spacecraft, making their space travel more comfortable.
Also, the spacecraft will conduct an experiment of fly-around and radial approach of rendezvous and docking with the orbiting space station core module.
Following that, the Shenzhou-12 will stay in-orbit and fly with the Tianhe core module for three months, marking another first in China's space history.
Unlike China's previous Shenzhou craft, which returned to Earth from an orbit of fixed altitude, Shenzhou-12 will be able to return from a range of orbital locations, a design that is aimed to enhance the craft's adaptability and reliability for its journey back to Earth.
The Shenzhou-12 crewed flight is believed by insiders to set a solid foundation for following space station construction missions which started in late April with the Tianhe core cabin launch and will last through 2022.
Next, the Tianzhou-3 cargo craft will be launched in September, and the Shenzhou-13 crewed spaceship will follow in October, according to CMSA director Hao Chun.
As the first manned space station mission, the Shenzhou-12 flight is of utmost significance due to its crucial role in connecting the previous 2 missions and the following legs in the 11 intensive construction schedule.
Setting up Wi-Fi, unboxing deliveries – Taikonauts busy 'housewarming' on their 1st ...
Setting up Wi-Fi, unboxing supplies delivered from Earth… the taikonauts are busy engaged in housewarming at their new home - ..
The new space race: Why China is on track to beat the US
Related posts:
We Chinese will have a home in space!: netizens applaud Tianhe space station core module launch
Tianzhou-2 cargo craft completes rendezvous, docking with China's space station core cabin at record speed
Chinese robotic spacecraft docks with the country's new space station"







