WHEN the wilfully unstoppable force of Nato expansion hits the steadfastly immovable object of Russian national security, war erupts.
`
By February 24 when Russian tanks rolled into Ukraine, Moscow’s challenges became exposed and grew more acute.
`
Russia cannot hold Ukraine in any sense as resentment to its incursion swells. There can be no assurance Russia can succeed in whatever it seeks to do to Kiev.
`
As in all military interventions, moving in is always easier than pulling out – which must eventually happen. And then what?
`
All disputes must conclude in negotiations, especially between neighbours, and it is now harder to negotiate. Meanwhile Russia is cast as the sole villain, so an invasion could not have been its preferred option.
`
As a power play it is a tragedy of Shakespearean proportions and superpower dimensions. Ukraine and Nato may have top billing but the US and Russia are the key actors.
`
The 1947 Dunkirk Treaty between Britain and France was a contingency agreement against German or Soviet aggression. This grew to include the Benelux countries and then the US and six others to become today’s North Atlantic Treaty Organisation.
`
By 1955 Nato expanded to include WWII foe Germany, leaving the Soviet Union out in the cold. Moscow then established its Warsaw Pact alliance in trying to achieve some balance.
`
Since then, Moscow stayed in Nato’s sights on the other side of the fence. Nato’s first Secretary-General Hastings Ismay described its role as “keeping the US in, Germany down, and Russia out.”
`
Nato is a Cold War device that was not dismantled after the Cold War but has instead grown. But the official rhetoric in the early 1990s was of consolidation with a few contemplating dissolution.
`
As the Soviet Union was collapsing in 1991, Nato officials from the US, Britain, France and Germany repeatedly assured Moscow that Nato would not expand. Nato had become the most serious organised challenge to Russian national security.
`
US Assistant Secretary of State Raymond Seitz said expansion of membership would not happen “either officially or unofficially.” His British counterpart added that expansion was “unacceptable”.
`
German Chancellor Helmut Kohl and Foreign Minister Hans Dietrich Genscher agreed and said so. Then Nato’s expansion happened.
`
When Russia complained, Nato stalwarts said any agreement was only verbal and not written down, implying that what they said could not be trusted. Later Nato claimed there had not even been a verbal agreement.
`
Earlier this month Germany’s Der Spiegel newspaper reported that Prof Joshua Shifrinson of Boston University had found a declassified document confirming that a pledge on Nato’s non-expansion had been made. Elsewhere it is reported that President Bill Clinton broke that pledge.
`
In 1999, Nato expanded by including former Soviet bloc countries Poland, Hungary and Czechia. Russia seethed but could do little.
`
In 2004, Nato expanded further by admitting former Soviet republics Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. Russia complained again but once more its security concerns were ignored.
`
As Nato missiles aimed at Russia moved closer to its borders, Moscow protested but Nato said they were only there because of Iran. Russia was unconvinced.
`
After Ukraine’s independence its government continued friendly relations with Russia. But the US engineered the 2004-05 Orange Revolution that toppled the government and replaced it with one closer to the West.
`
France and Germany invaded Russia in the 19th and 20th centuries with each attack ending in disaster. Napoleon’s and Hitler’s forces nonetheless made damaging incursions into the Russian heartland and national psyche.
`
Today France and Germany are among European nations careful in managing relations with Russia. However, a US-led Nato with less experience and less sensitivity to Russian security concerns has acted with less care.
`
Russia remains the world’s largest country by area rich in natural resources like oil and gas. It is not a threat to Europe or even Ukraine if agreements made can be honoured, but provoking it can produce a different result.
`
Using Nato to challenge and undermine Russian interests will not end well for anyone. US interests are protected with the Atlantic Ocean as buffer, but European members of Nato share a continent with Russia and would have different priorities.
`
The UN wants Russian forces to withdraw from Ukraine and return to base almost as much as Russia wants Nato to withdraw from its eastward momentum and return to the 1997 Nato-Russia Founding Act. Although neither may happen soon, Moscow has no interest or expressed desire to occupy Ukraine so the former is more likely than the latter.
`
Ukraine for now is trapped in a vicious cycle of violence and disintegration beyond its control. It is a familiar plight of pawns caught between incompatible great powers.
`
Ukraine wants urgent negotiations with Russia while Russia wants Belarus to host talks on the Minsk accords for a ceasefire and phased measures towards a compromise. Even if talks are possible it will be an uphill task since Moscow and Kiev have different interpretations of the 2014-15 terms.
`
Among Biden’s errors is targeting Putin personally as if another Russian leader would have acted differently. Even Boris Yeltsin would have done the same over Ukraine, while a nationalist like Vladimir Zhirinovsky would have acted tougher and earlier.
`
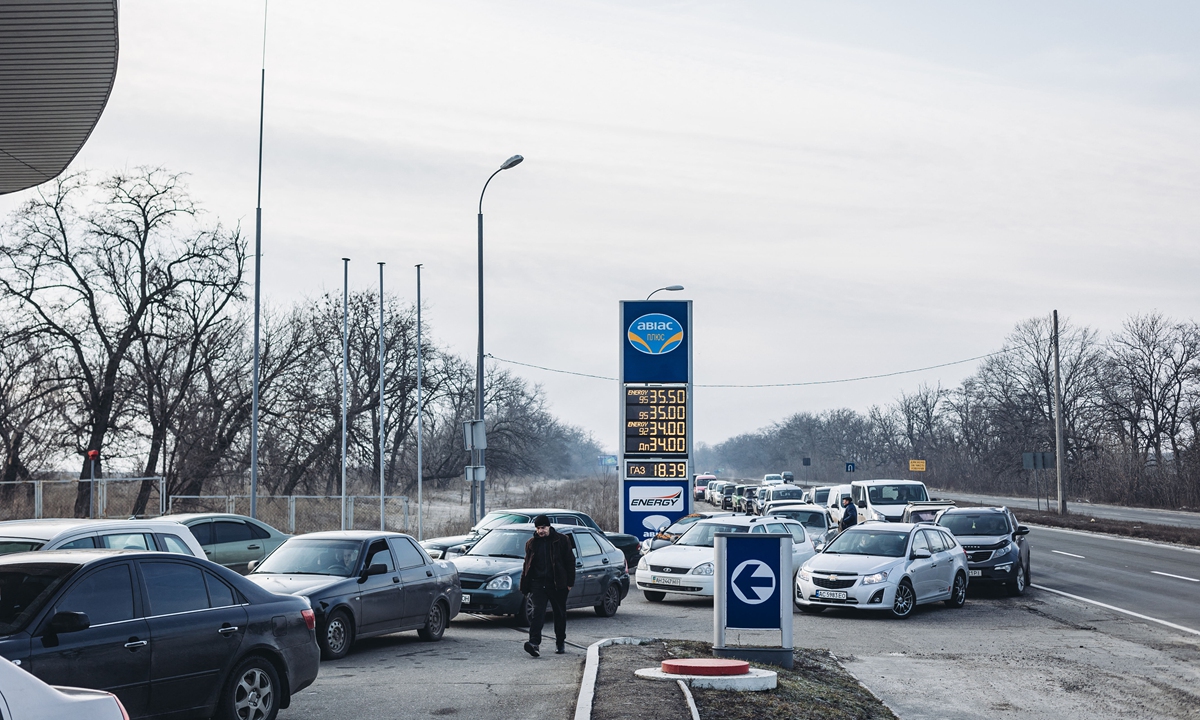
For the West to dump the Nord Stream 2 deal supplying Europe with Russian gas punishes only Europe which now has to pay many times more for US supplies. On Feb 4 Russia signed a new US$117.5bil oil and gas deal to supply China instead.
`
Western observers worry that China may learn unsavoury lessons from Russia’s actions in Ukraine to further its disputed claims in Asia. Any lessons would be more akin to Nato’s gradual encroachment on Russian territory.
`
The apparent beneficiary from Ukraine’s crisis is China, being a distraction for the West which also increases Moscow’s dependence on Beijing. But China is also awkwardly positioned as it wants to maintain good ties with all parties.
`
The only unqualified beneficiary of the crisis is China-Russia relations, which must count as another major strategic blunder for Nato and the West.
`
Bunn Nagara is a political analyst and Honorary Research Fellow of the Perak Academy. The views expressed here are solely the writer’s own.


Is Ukraine a metaverse nightmare?
`
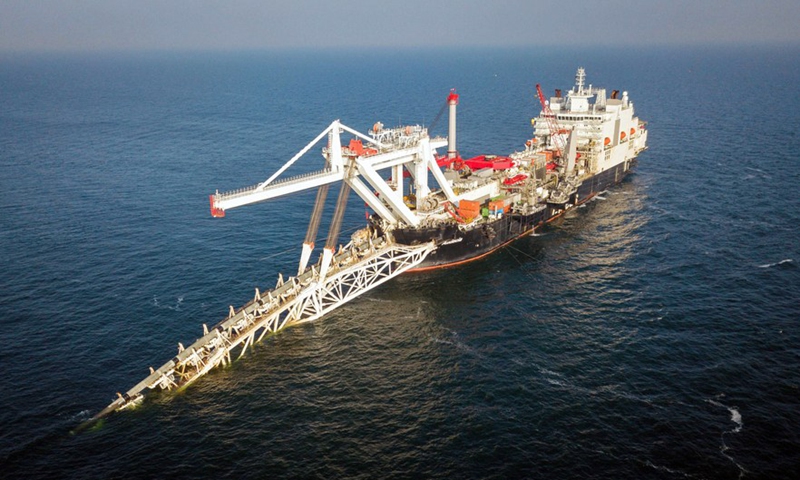
The Russian pipe-laying ship 'Akademik Tscherski' which is on deployment for the further construction of the Nord Stream 2 Baltic Sea pipeline, is moored at the port of Mukran on the island of Ruegen, Germany, on Sept. 8, 2020. The gas is still flowing from Russian even as bullets and missiles fly in Ukraine. But the war is raising huge questions about the energy ties between Europe and Russia. The conflict is helping keep oil and gas prices high due to fears of a possible reduction in supplies, and consumers will continue to face financial stress from that.
The real-life cost of war: People walk at the border crossing between Poland and Ukraine, in Medyka, Poland, on February 24, 2022. Photo: Reuters
Moving from a unipolar world to a multipolar world was always likely to be messy and risk-prone. But few saw how fast we moved from beating war drums to actual armed conflict between the Great Powers, the latest being in Ukraine. Are we on a march of folly to World War III, or have key players lost sight of reality?
`Lest we forget, World War I (1914-1918) and World War II (1939-1945)
were fought to keep down rising powers—Germany and later Japan.
`
Russia and China suffered the most casualties in WWII, and both were allies against German Nazis and Japanese militarists.
`
The United States became the real winner, but decided after WWII to contain communism in both the Soviet Union (USSR) and China.
`
Fifty years ago, in 1972, US President Nixon set aside enmity against China, restored US-China relations, and in one strategic stroke, isolated the Soviet Union, leading to its collapse two decades later.
`
The great achievement during the Cold War was the avoidance of nuclear conflict, with the Cuban missile crisis being a live test of brinkmanship.
`
Both sides climbed down when the USSR removed missiles from Cuba, and the US quietly removed missiles from Turkey.
`
President Kennedy understood that grandstanding on moral issues should be restrained, because in a nuclear war, mutually assured destruction is madness.
`
After seven decades of peace, the Western media has been painting the multipolar world as a black-and-white conflict between good vs evil, democracy vs autocracy—without appreciating that the other side may have different points of view that need to be heard.
`
By definition, a multipolar world means that liberal democracies will have to live with different ideologies and regimes.
`
Today, YouTube and the Web provide a wealth of alternative views than mainstream media, such as CNN or BBC.
`
Prof John Mearsheimer, author of the influential book "The Tragedy of Great Power Politics," offers the insight that the Western expansion of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (Nato) was the reason why Russia felt threatened.
`
The more the Nato allies try to arm Ukraine, the more insecure Russia gets.
`
In essence, Russia wants a buffer zone of neutral countries like Austria, which are not members of Nato, but that does not exclude trade with all sides.
`
Carnegie Moscow Center analyst Alexander Baunov described how "the two sides appear to be negotiating over different things.
`
Russia is talking about its own security, while the West is focusing on Ukraine's."
`
What he is describing are two sides that are each in their own social bubble or virtual reality (VR) Metaverse, deaf to the other side's views.
`
The term "Metaverse" came from a 1992 dystopian sci-fi novel titled "Snow Crash," where the Metaverse is the virtual refuge from an anarchic world controlled by the Mafia.
`
Today, Metaverse is an online virtual world where the user blends VR with the real, flesh-and-blood world through VR glasses and software augmented reality (AR).
`
In other words, in Metaverse, your mind is colonised by whatever algorithm and virtual information that you get—real or fake news.
`
Metaverse is escapism from reality, and will not help us solve real world problems, especially when we need to talk eyeball to eyeball.
`
The Metaverse designer is more interested in controlling or influencing our minds, feeding us what we want to hear or see, rather than what information we need to have to make good decisions. The risk is that we think VR conflict is costless, whereas real war has real flesh-and-blood costs.
`
.In short, the more we look inward at our own Metaverse, the more we
neglect the collective costs to the world as it lurches from peace to
war
`
Surprisingly, I found the right-wing influential Fox commentator Tucker Carlson asking better questions than CNN or BBC commentators.
`
In his show Tucker Carlson Tonight, in the segment "How will this conflict affect you?" he asked bluntly why Americans should hate Putin and what the war will cost every American.
`
Carlson asked some really serious questions, even though his views are partisan—have the Democrats, with their moral concern to hate Putin, forgotten the big picture of war costs?
`
First, would Americans be willing to go into a winter war with Russia?
`
Second, would they pay much higher gas prices as oil prices have already hit above USD 100 per barrel?
`
Although economic sanctions are applied, even Europe will not be willing to risk cutting off gas supplies from Russia, since Russia accounts for 35 percent of European gas supplies.
`
Third, is Ukraine a real democracy?
`
Carlson's 2018 book "Ship of Fools: How a Selfish Ruling Class Is Bringing America to the Brink of Revolution" is well worth reading to understand how conservative Americans think about elites who care about themselves more than society at large.
Carlson asked some really serious questions, even though his views are partisan—have the Democrats, with their moral concern to hate Putin, forgotten the big picture of war costs?
`
First, would Americans be willing to go into a winter war with Russia?
`
Second, would they pay much higher gas prices as oil prices have already hit above USD 100 per barrel?
`
Although economic sanctions are applied, even Europe will not be willing to risk cutting off gas supplies from Russia, since Russia accounts for 35 percent of European gas supplies.
`
Third, is Ukraine a real democracy?
`
Carlson's 2018 book "Ship of Fools: How a Selfish Ruling Class Is Bringing America to the Brink of Revolution" is well worth reading to understand how conservative Americans think about elites who care about themselves more than society at large.
`
In sum, the decade of 2020s may face a tough period of escalating conflicts at local, regional and global levels, with proxy wars that disrupt each other's economies and social stability.
`
If states fail, and poor and hungry people migrate at a larger scale, even more border conflicts are likely, since most will want to go to the richer countries in the North, such as Europe and America.
`
There is no ideal world where everyone is good and the other side is bad.
`
In a multipolar world, there will be all kinds of people that we don't like, but we have to live with them.
`
A negotiated peace is better than mutual destruction.
`
In Metaverse, virtual life can be beautiful, moral and perfect, but the real world is lurching towards a collective nightmare.
`
We should not kid ourselves that the Metaverse VR of self-deception is the real world.
`
We either sleepwalk to war, or have the courage to opt for sustainable peace.
`
The real question is: Who is willing to climb down and eat the humble pie for the sake of peace?
`
By Andrew Sheng is adjunct professor at Tsinghua University, Beijing and the University of Malaya. He was formerly the chairman of the Securities and Futures Commission, Hong Kong.
 Tan Sri Andrew Sheng (born 1946) is Hong Kong-based Malaysian Chinese banker, academic and commentator. He started his career as an accountant and is now a distinguished fellow of Fung Global Institute, a global think tank based in Hong Kong.[1] He served as chairman of the Hong Kong Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) before his replacement by Martin Wheatley in
Tan Sri Andrew Sheng (born 1946) is Hong Kong-based Malaysian Chinese banker, academic and commentator. He started his career as an accountant and is now a distinguished fellow of Fung Global Institute, a global think tank based in Hong Kong.[1] He served as chairman of the Hong Kong Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) before his replacement by Martin Wheatley in
Andrew Sheng comments on global affairs from an Asian perspective. The views expressed here are his own.
Related posts:
Black smoke rises from a military airport in
Chuguyev near Kharkiv on February 24, 2022, after Russian President
Vladimir Putin announced a...
` ` MAN and nature are running out of time. That’s the core message of the UN Inter-governmental Panel on Climate Change
...
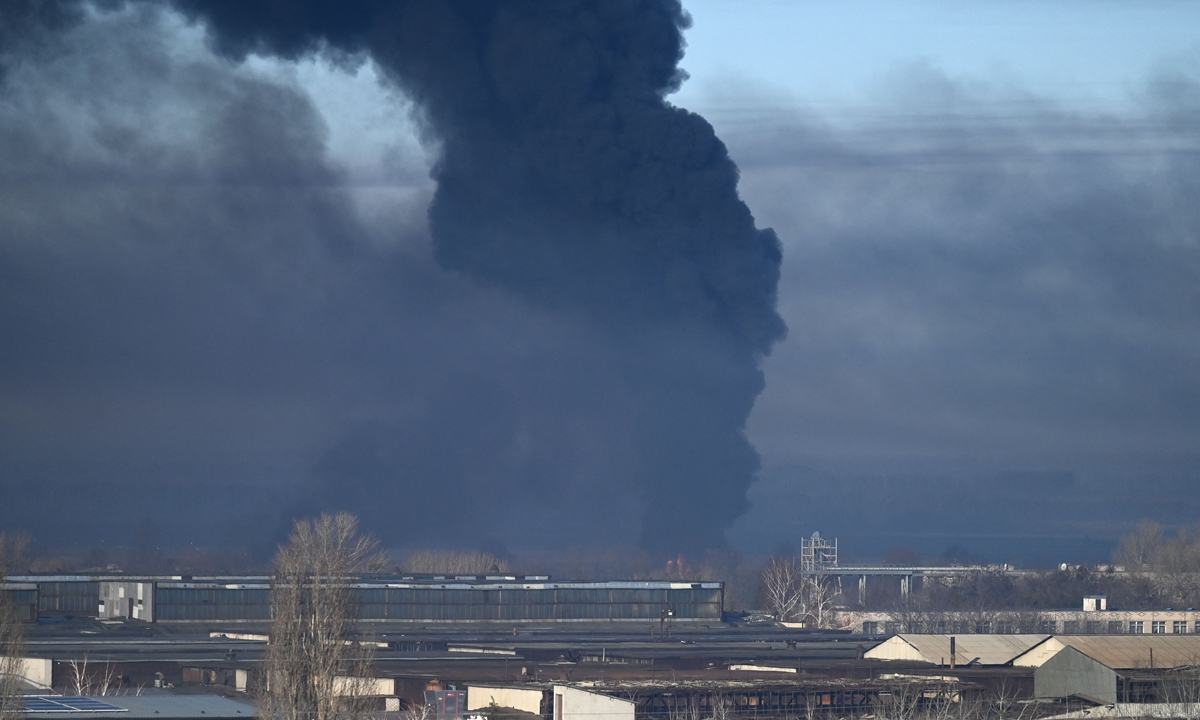














 Black smoke rises from a military airport in Chuguyev near Kharkiv on February 24, 2022, after Russian President Vladimir Putin announced a military operation in Ukraine. Photo: VCG
Black smoke rises from a military airport in Chuguyev near Kharkiv on February 24, 2022, after Russian President Vladimir Putin announced a military operation in Ukraine. Photo: VCG