The responsible lending guidelines, among the pre-emptive measures by Bank Negara to contain surging household debt, have made a strong impact on most people. Will the guidelines be effective to control the alarming levels of household debt and put the brakes on loan growth? THE responsible lending guidelines, which came into effect on Jan 1, created quite a stir in the
banking industry with leading indicators signalling further signs of loan growth slowing in the coming months.
There is some discontent among consumers in terms of having their loans approved based on net income compared with gross income previously, in addition to which is the need for more documentation.
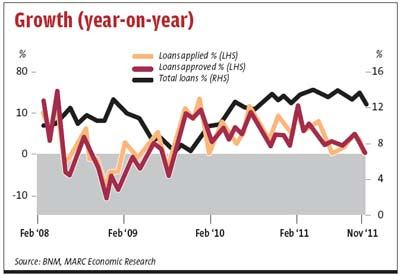
Some automotive players and property developers are not too happy either as they feel the move will be a dampener to their business moving forward. Loan growth for January was lower at 12.1% year-on-year (y-o-y), probably the slowest since 2010, compared with 13.6% y-o-y in December last year mainly due to slower growth in the household and business segments.
Total application and approval for loans in January was down almost 3% from a year ago although those disbursed rose by 5.6% y-o-y.
Loans in the household sector, which has a high level of
indebtedness, was dragged down by slower growth in auto, mortgage and personal loans. But some quarters argue that this could be attributed to shorter working days in January due to the
Lunar New Year break and other holidays.
Officials say that a loan growth in the region of 12% appears to be fine and much stronger growth may be a problem if left unchecked.
Indications are that loan growth to households, which was lower in 2011 than 2010, will normalise in February this year after the dip in January.
Whatever the arguments are, this trend, if it does continue, can be seen by some quarters as worrisome. Will loan growth then continue to slide? Some industry observers and analysts think so.
Loan growth mixed signalsUnder the guidelines, banks are, among others, required to apply the net-income calculation method instead of gross income when computing the
debt-service ratio for potential borrowers. The lending guidelines cover housing, personal and car loans,
credit cards, receivables and loans for the purchase of securities.
 Malaysian Rating Corp Bhd
Malaysian Rating Corp Bhd chief economist Nor Zahidi Alias says based on indicators, the rating agency feel that loan growth will likely moderate this year to a single-digit figure compared with a 13.6% growth recorded last year.
Nor Zahidi says the stricter guidelines is a step in the right direction.This is due to the fact that some potential borrowers will no longer be eligible for certain
types of loans, he says. This, he adds, is evidenced by a steep drop in the volume of passenger cars sold in January by 25% compared with the same period last year following stricter hire-purchase loan processes.
Total vehicle sales, however, rebounded by 9% in February with industry sales hitting 44,013 units from 40,387 units in February 2011.
Going forward, Zahidi says he foresees further decline in the banking sector loan growth as banks continue to be extra prudent in their lending practices, adding that there are also declines in loan applications for cars, credit card and residential properties based on latest indicators.
Loan applications for purchases of passenger cars contracted by 15.5% in January from 7.8% growth in December 2011. Another significant drop was the application for the amount given to the credit card segment which fell by 50.9% in January from a decline of 10.2% in December 2011. Applications for loans for the purpose of purchasing residential properties contracted 6.3% from a growth of 11.3% in December 2011.
Approvals for loans categorised for “personal uses” declined by 29.8% compared with a 42.4% growth in December 2011 while the amount of loans approved for the purchase of passenger cars and residential properties contracted by 18.4% and 20.9% respectively in January (December 2011: 0.3% and 1.8% respectively).
The Association of Banks in Malaysia (
ABM) says the implementation of the guidelines will not have a direct relation to its member banks' loan growth. Factors like global economic conditions and its impact on the regional economy as well as developments on the external and domestic front will be the more pertinent factors that will have an effect on loan growth, it says.
“The guidelines merely set out to better define the expectations of banks to act responsibly and transparently when lending. The policies and practices envisaged are not entirely new as they underscore the existing approach taken by our members. While it will ensure that the debt commitments of individuals and households are within their repayment capabilities, customers who can afford to repay will not be denied access to
financing,” it says.
A robust retail finance market, ABM says, cannot be measured by loan growth alone as the obligations (financial and contractual) to repay, sound personal financial management skills and responsible financing practices are more important to the stability and sustainability of the market in the long run.
Weaker numbersThe occurance of non-performing loans and loans in arrears appear to be falling, and they are what bankers and regulators are paying close attention to. That will indicate that the responsible lending guidelines, even though they may crimp the longer-term trend, is not having an impact on the quality of existing loans.
 Wong expects loan growth to taper to 8%-9% after clocking in a strong 14% last year.
Wong expects loan growth to taper to 8%-9% after clocking in a strong 14% last year.
CIMB Research says in one of its notes that it expects a slowdown in loan growth this year due to weaker numbers from all major loan segments including residential mortgages and auto loans.
RHB Research Institute considers that on the whole, the new guidelines will have some impact on household loan growth, but the extent of the impact remains to be seen.
As for demand for loans from the household segment, the research outfit does not think the growth will fall off the cliff, but rather will be at a more moderate pace relative to recent years.
Jupiter Securities head of research Pong Teng Siew feels that with the strict adherence to the lending guidelines, loan growth may hit 8% or less sometime later in the year but may pick up in some months.
OSK Research is maintaining its loan growth projection for this year at 9% despite the guidelines which it says will play a part in slowing loan growth. The projection was underpinned by
Economic Transformation Programme (ETP) projects.
RAM Ratings head of financial institution ratings Wong Yin Ching expects loan growth to taper to 8%-9% after clocking in a strong 14% last year.
This, she says, will be supported by expectations of a real gross domestic product growth of 4.6% in 2012 (2011: 5.1%) and a more moderate household loan growth due to various prudential measures introduced since late-2010. Loans growth is said to be correleated to economic growth and with the Government seeing growth to come in at 4%-5% this year, expectations are that the pace of loans given out will accelerate at a slower pace.
Wong says the loan growth will be partly balanced by stronger financing demand from the corporate and commercial sector in anticipation of the rollout of projects under the ETP and 10th Malaysia Plan gaining momentum.
Meanwhile,
Maybank IB Research, with a neutral call on the banking sector, says it expects domestic loan growth of 10.5% this year, up from its previous forecast of 9.4%, adding that mortgage lending is expected to hold up better than anticipated.
According to Bank Negara's Financial Stability and Payment Systems Report 2011, the growth of household debt to gross domestic product (GDP) increased last year but the pace was slower with outstanding household debts expanding by 12.5% to 76.6% for the year compared to 2010 when debt grew 13.7% to 75.8%.
It adds that signs of stabilisation in household debt relative to GDP was seen from the second half of last year after a continued upward quarterly trend observed since 2009 with borrowing continuing to be concentrated on residential properties and motor vehicles, which together account for 64% of total household debt.
The report states that bank lending to individuals earning more than RM3,000 per month accounted for about 80% of total loans to households by the banking system.
 Choo says the guidelines will not have any adverse impact on those with genuine capacity to repay.
Choo says the guidelines will not have any adverse impact on those with genuine capacity to repay.It adds that bank exposure to borrowers with monthly incomes of RM3,00 or less was relatively low representing less than 13% of total banking system loans. “Based on historical experience on the level of impairment and provisioning, any impairment losses to banks are not likely to exceed RM2bil or less than 8% of pre-tax profits of commercial and Islamic banks,” it notes.
The growth in household debts had also been accompanied by a corresponding expansion in household financial assets, it says, adding that stronger growth in household deposits which expanded by 12.2% balanced the slower increase in financial assets.
Timely move?Despite the brouhaha surrounding the pre-emptive measure, many feel the introduction of the guidelines is timely and justifiable.
RAM's Wong views it as one of the many measures to contain the growth of household debt.
The banking system's household financing has been rising steadily over the last five years and currently constitutes about 55% of the system's total financing, she says, noting that the growth has stemmed mainly from home and personal loans.
As a result, she says, Malaysia's household debt-to-GDP ratio has trended upwards from 69% in 2006 to 77% in 2011. Compared to other countries in the region, this figure is considered high especially when looked at in relation to GDP per capita, she adds.
Some of the other pre-emptive measures which Bank Negara had earlier imposed to control rising household debt include tighter criteria for residential property financing, such as a 70% loan-to-value (LTV) cap on a borrower's third housing loan and beyond, as well as raising the income eligibility criteria for credit cards.
Some analysts concur that the lending guidelines are vital to ensure quality loan growth and some form of control is necessary. With ringgit deposits slowing, analysts expect banks to start pulling back on lending even in the absence of the guidelines.
Zahidi says the guidelines are introduced to ensure that the consumer segment will not be overstretched for too long. While it will take a few years before Malaysia's household debt can be reduced to below 60% of GDP, the stricter guidelines is a step in the right direction, he says.
However, he adds that this will have some adverse effects on the banking sector's loan growth as well as on private consumption.
OCBC Bank (M) Bhd country chief risk officer Choo Yee Kwan says credit assessments under the guidelines are done holistically by taking into account the total debt obligations of an individual borrower and will not have any adverse impact on those with genuine capacity to repay.
At the same time, he says, it will help to deter borrowings for speculative purposes and align debt burden more closely with repayment capacity.

Cavale says the long-term impact on banks is yet to be determined.“While the guidelines are relatively prescriptive on the lending approach, they are really complementary when viewed from the vantage of a bank with more advanced risk assessment tools and portfolio screening and early warning triggers for sustainable loan portfolio health,” Choo explains.
A banking analyst from MIDF Research, on the other hand, thinks that while the guidelines on the whole are good, some details are vague and not properly spelt out. For example, there is no mention of specific details on liability as well as on debt servicing ratio, and is left to individual banks to assess the risk appetite of loan applicants.
managing director for cards and consumer lending Anand Cavale feels that while the guidelines will strengthen the control for lending, the long-term impact on banks is yet to be determined.
Although it will help reduce the level of household debt, this will depend on the state of the economy, as household debt is directly linked to the performance of the country's economy, he says.
While the guidelines will strengthen the overall ability to lend prudently, Cavale believes there should be proper infrastructure in place. For example, banks having accessible ways to the customer income information will help the process to implement the guidelines more smoothly, he points out.
Some analysts feel the stringent lending guidelines may cause banks to shift their focus to other areas to boost their bottomlines.
The MIDF Research analyst says banks may, for example, look to increase high net worth individuals or affluent customers for their credit cards as in the case of
. This, he adds, will include cross selling of cards to this segment.
For the mortgage side, banks may look into issuing more financing for landed properties in selected locations and for the auto business, they may source for stronger dealership, the analyst says.
Choo says OCBC Bank's objective is to derive 30% of its income from non-interest income sources, noting that it is keen to diversify and strengthen its deposit base to ensure it is not overly concentrated in any one specific segment.
According to Cavale, it is likely that banks will add other products or services that will support additional streams of income to mitigate potential reductions in the lending area.
Another area which banks are aggressively pursuing currently is the small and medium enterprise (SME) segment. This segment, according to an analyst with an investment bank, will provide better margins and probably make up for the shortfall in slower loan growth from the stringent guidelines.
Those banks which were not focusing on the SME segment will now have to employ strategies to capture this growing segment, he adds.